Everything you need to know about e-invoicing in SAP

What is e-invoice?
E-invoice or electronic invoice is a type of invoice that is created by a computerized system. It is not printed on paper, it is hundred percent digital. As countries adopt use of structured electronic invoices for tax audit purposes, they set XML or JSON as the standard file format. For that reason nowadays pdf invoices are not usually classified as electronic invoices.
How to generate e-invoice?
Although the governments usually allow taxpayers to create e-invoices manually on the tax authority portal in XML or JSON format, it requires a lot of effort and time to manage it. For these reasons, it is necessary for the organizations with a lot of transactions to automate the e-invoice generation. It can be realized via using an e-invoicing software which is able to create mass amounts of e-invoices without human intervention. This software must be able to extract the transaction data from an ERP system such as SAP.
Extensible Markup Language (XML) is a text format with a defined set of rules that is both human-readable and machine-readable. JavaScript Object Notation (JSON) is a similar text format but instead it uses syntax of JavaScript programming language.
Advantages of E-invoicing
There are proven e-invoicing benefits for companies, governments and the public sector:
- Companies effectively reduce costs, facilitate automation, enhance compliance, save time, reduce carbon footprint and shorten payment cycles.
- Governments implement e-invoicing policies to facilitate stricter tax audit, increase efficiency in tax collection and reduce VAT fraud and VAT gap.
- The adoption of e-invoicing in the public sector reduces public sector deficit and costs, increases efficiency and financial transparency, and promotes sustainable development. Thus it increases the economic well-being of people.
Is e-invoice mandatory in your country?
In every part of the world, particularly in Latin America, Europe and Asia, the electronic invoices are regulated by law. Taxpayers are allowed to use it instead of paper invoices. In some countries it requires the buyer’s consent. In some of them, electronic invoicing between taxpayers (B2B e-invoicing) is mandatory:
Italy, Turkey, Egypt, Kazakhstan (EMEA)
Indonesia, South Korea, Taiwan (Asia)
Brazil, Mexico, Argentina, Chile, Peru, Colombia, Costa Rica, Guatemala (LATAM)
In addition, the EU Directive 2014/55/EU on electronic invoicing in public procurement, forced central and non-central government entities in Europe to adopt e-invoicing in 2019 and 2020, respectively. Almost all of the European countries have succeeded in setting up a national e-invoicing system by the end of 2020. Many of them including Germany, Portugal, France, Italy, Netherlands, Finland, Norway, Spain and Belgium also mandated B2G e-invoicing for government suppliers.
E-invoice Implementation Dates
1 January 2021 Portugal, B2G (PDF accepted until 30 June 2021)
1 April 2021 India, B2B (taxpayers with turnover between Rs 50 and 100 Crore)
15 May 2021 Egypt, B2B 3rd Phase (more than 2000 companies)
1 July 2021 Albania, B2B
1 July 2022 Serbia, B2G (draft law)
4 December 2021 Saudi Arabia
1 July 2022 Vietnam
1 July 2022 – Serbia, B2B (draft law)
2022 Romania
1 January 2023 France, B2B (large companies)
1 january 2023 Poland
2023 Philippines
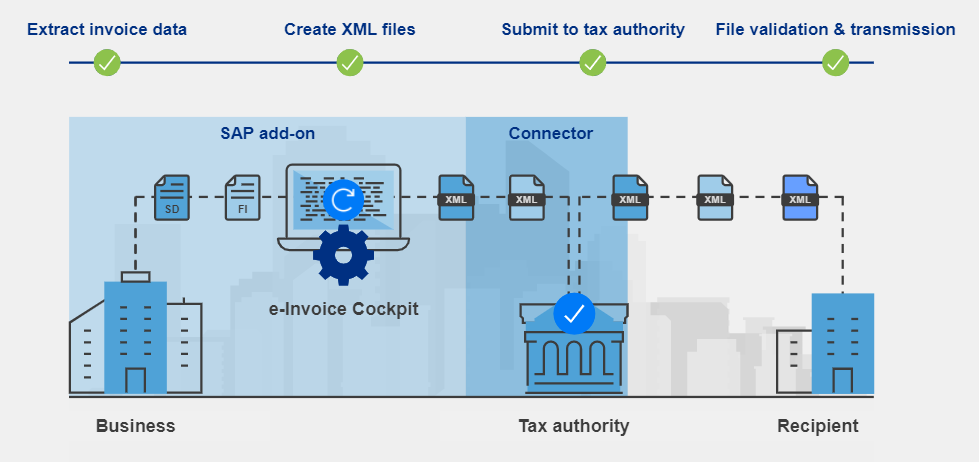
What is e-invoicing in SAP?
There are third party e-invoicing solutions integrated with SAP which can manage e-invoicing in SAP: To accomplish this, first tax type codes are mapped into SAP tax codes. Invoice data is manually or automatically extracted from SAP modules to an SAP Add-On. Finally, e-invoicing software transforms the information into desired electronic formats such as XML or JSON in the Add-On.
Why SAP e-invoicing for compliance?
Using an SAP Add-On solution for e-invoicing which is able to process the invoice data within SAP is very important for the privacy and security of your client data. Such a solution does not take your customer data out of your SAP system. It can generate e-invoices automatically without human intervention and apply electronic signature whenever required. Eventually, data security and integrity are maintained according to the requirements of tax authorities. These qualifications are very effective in tax compliance.